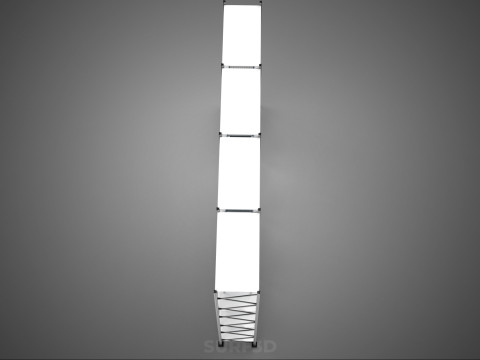
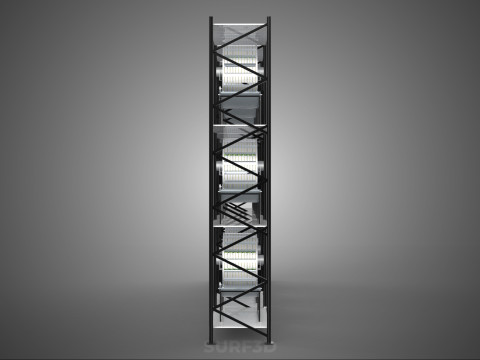
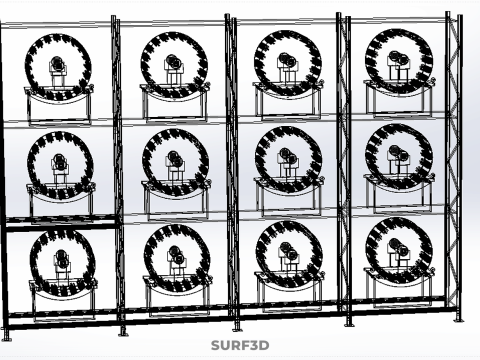
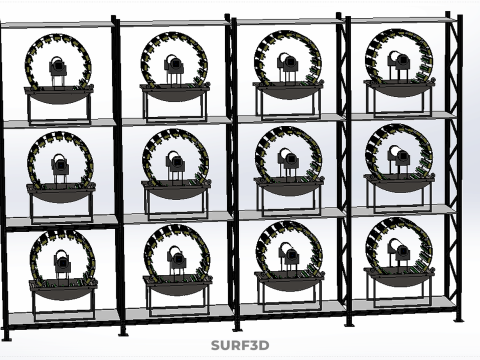
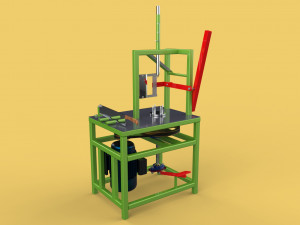
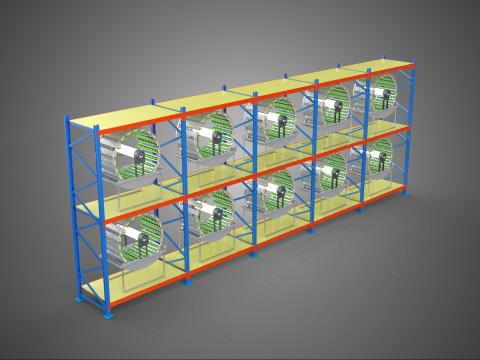
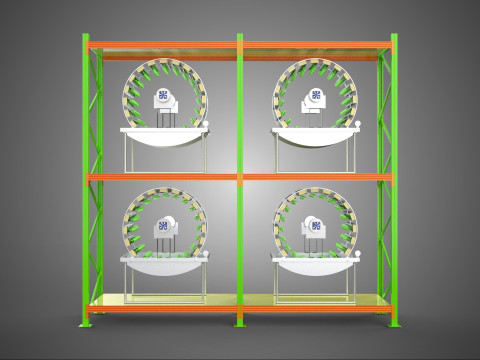
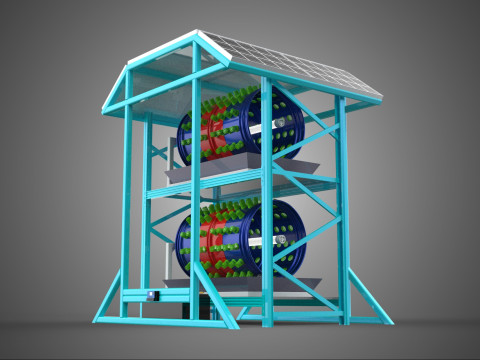
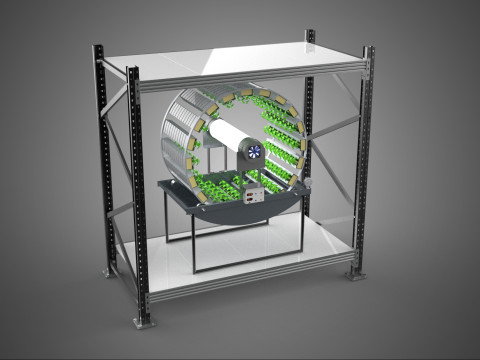
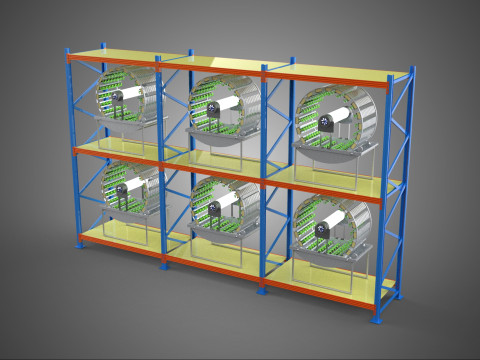
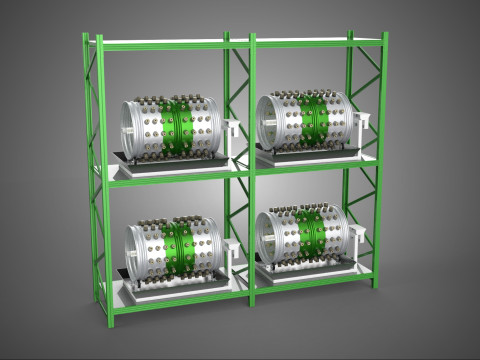
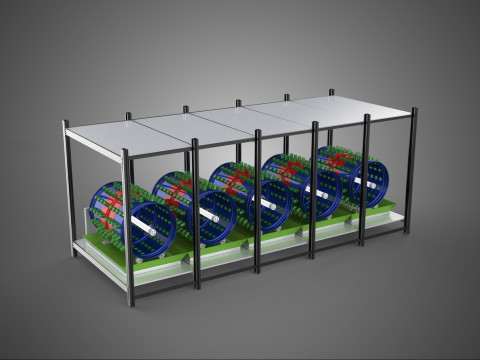
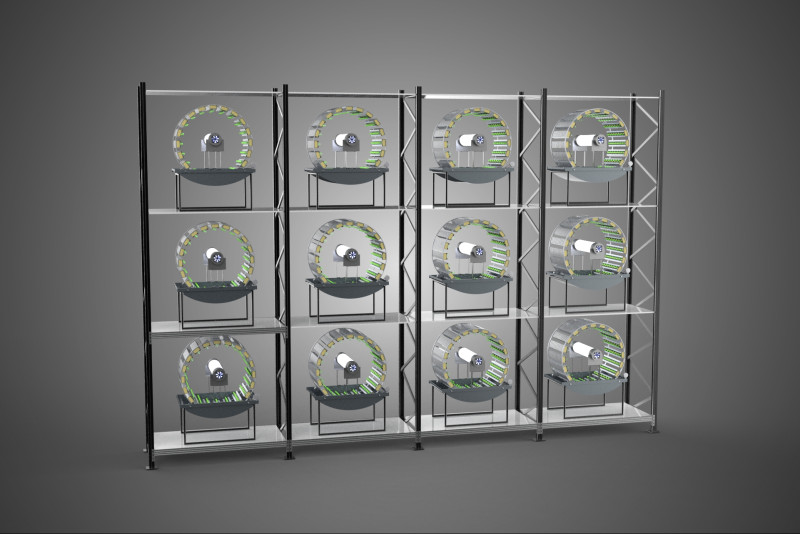
VERTICAL SHELF RACK TRAY ROTARY HYDROPONIC PLANT GARDEN TOWER 3D 模型

- 可用的格式: IGES (.iges) 3.97 MB3D Studio (.3ds) 28.97 MBBlender3D (.blend) 103.06 MBStereolithography (.stl) 95.03 MBSTEP (.step) 3.95 MBAutodesk FBX (.fbx) 166.76 MBAutodesk 3DS MAX (.max) 185.60 MBWavefront OBJ (.obj) 100.78 MBAutodesk AutoCAD (.dwg) 37.98 MBRhinoceros (.3dm) 7.96 MBGLB (.glb / .gltf) 38.40 MBACIS(.sat) 63.61 MBCollada (.dae) 118.08 MBSketchUp (.skp) 2.88 MB
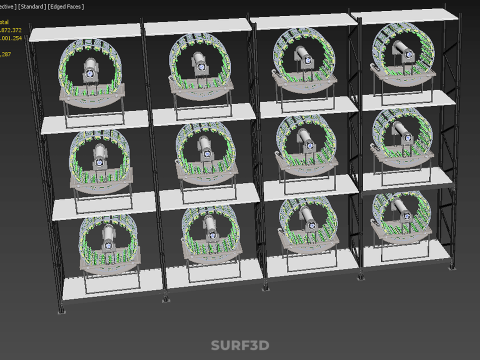
- 多边形:7872372
- 顶点:6001254
- 动画:No
- 纹理:No
- 操纵:No
- 材料:
- 低聚:No
- 集合:No
- UVW 贴图:No
- 使用插件:No
- 打印准备:No
- 3D扫描:No
- 成人内容:No
- PBR:No
- 人工智能培训:No
- 几何:Poly NURBS
- 包装 UVs:Unknown
- 日期:167
- 日期: 2025-09-30
- 项目 ID:602354
High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely supported formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software support
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
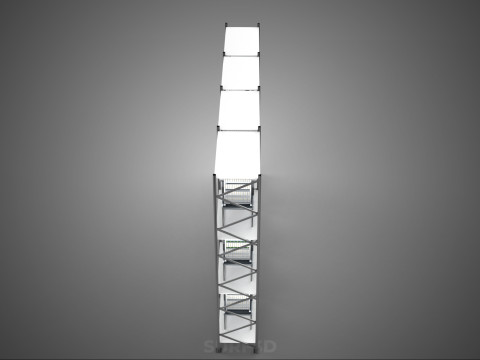
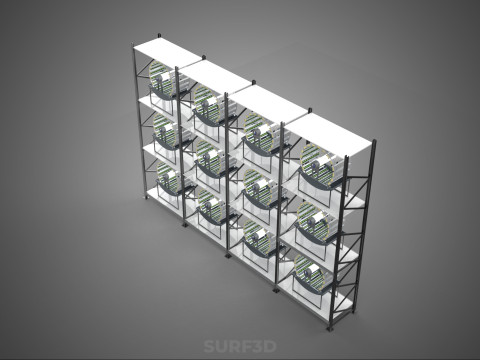
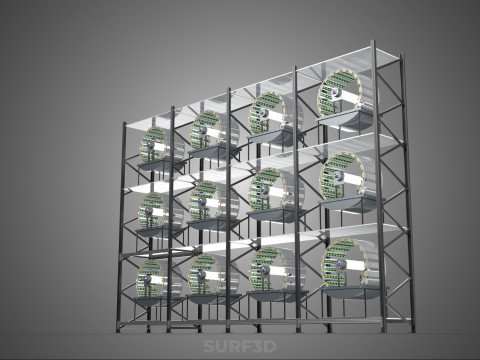
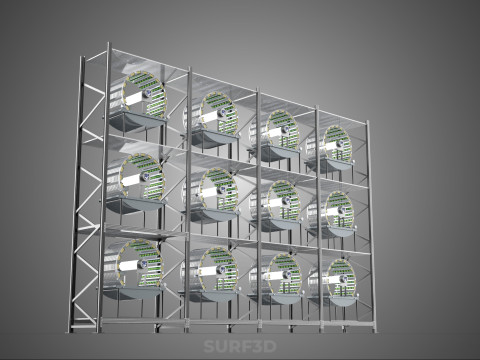
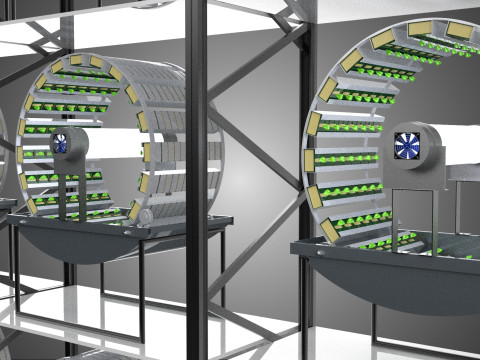
A "Vertical Shelf Rack Tray Rotary Hydroponic Plant Garden Tower" is an advanced, controlled-environment agricultural system designed for highly efficient and space-optimized cultivation of plants using hydroponic methods. This technology integrates vertical farming principles with a dynamic mechanical rotation mechanism, allowing for maximized plant density and resource utilization within confined spaces. It represents a sophisticated approach to sustainable agriculture, particularly relevant for urban farming, research, and high-yield commercial production.
**Core Components and Structure:**
The system is fundamentally composed of several interconnected elements:
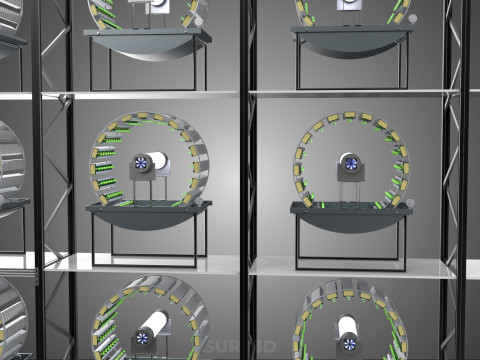
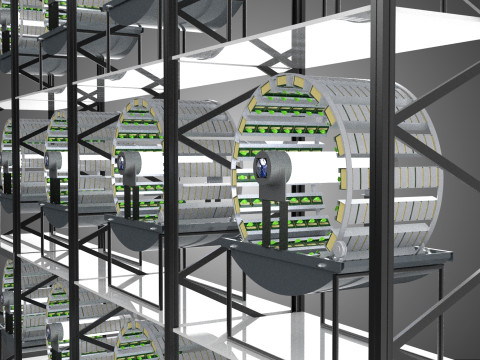
1. **Vertical Frame/Structure:** A robust, often modular, framework that supports multiple tiers or shelves of growing plants. This structure is engineered for stability and to house the various operational components.
2. **Shelf/Rack/Tray System:** These are the individual growing levels, typically configured as shelves, racks, or distinct trays made from food-grade, inert materials. They hold the plants, often in net pots with an inert growing medium (e.g., rockwool, coco coir, clay pebbles), and facilitate the circulation or containment of nutrient solution. These levels are stacked vertically, often in a columnar or tiered arrangement around a central axis.
3. **Rotary Mechanism:** This is the defining feature, comprising a central shaft, an electric motor, and a gearing system that facilitates the slow, continuous, or intermittent rotation of the entire vertical stack of trays or individual plant holders. The rotation speed is typically very low, measured in rotations per hour or day.
4. **Hydroponic System:** Integrated within the structure, this system delivers nutrient-rich water directly to the plant roots. It includes a reservoir for the nutrient solution, a pump for circulation, tubing, and emitters (which may utilize methods such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), or drip irrigation) to distribute the solution to each growing tray.
5. **Lighting System:** As these towers are frequently deployed indoors or in environments with insufficient natural light, artificial grow lights (predominantly energy-efficient LEDs) are essential. These are typically positioned centrally or strategically around the rotating structure to ensure uniform illumination.
6. **Environmental Control Unit:** Advanced systems incorporate sensors and controllers to monitor and regulate environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, nutrient solution pH, and Electrical Conductivity (EC).
**Operational Principles:**
Plants are cultivated without soil, relying solely on the nutrient-rich water delivered by the hydroponic system. The unique aspect of the rotary design is its ability to optimize critical growth factors:
* **Uniform Light Exposure:** By rotating the plants past stationary light sources, each plant receives equitable and consistent light intensity and duration, preventing etiolation (stretching due to insufficient light) and promoting symmetrical growth. This eliminates the need for moving light fixtures or repositioning plants manually.
* **Nutrient Cycling and Distribution:** The rotation ensures that all plants on a given level receive equal access to the circulating nutrient solution, preventing localized depletion or over-saturation.
* **Maximized Space Utilization:** The vertical stacking drastically increases the plant density per unit of floor area, making it exceptionally efficient for environments with limited horizontal space.
* **Enhanced Accessibility and Maintenance:** The rotation can bring all plants to an accessible point for inspection, harvesting, pruning, or pest management, significantly reducing labor and improving operational ergonomics.
**Advantages:**
* **Exceptional Space Efficiency:** Ideal for urban settings, apartments, and commercial facilities with constrained footprints.
* **Optimized Resource Consumption:** Hydroponics uses significantly less water than traditional soil-based agriculture, and the enclosed nature of many towers minimizes evaporation.
* **Accelerated Growth and Higher Yields:** Controlled environmental conditions, precise nutrient delivery, and uniform light exposure often lead to faster growth cycles and greater crop output per square foot.
* **Reduced Pest and Disease Incidence:** The controlled indoor environment minimizes exposure to external pests, pathogens, and environmental contaminants.
* **Consistent Product Quality:** Uniform growing conditions contribute to standardized plant development, leading to predictable and high-quality produce.
* **Automation Potential:** Many aspects, including nutrient delivery, lighting cycles, and rotation, can be automated, reducing manual labor requirements.
**Disadvantages and Considerations:**
* **Higher Initial Investment:** The cost of acquiring and installing a rotary hydroponic tower is generally higher than simpler hydroponic systems or conventional gardening.
* **Technical Complexity:** Requires a foundational understanding of hydroponics, mechanical systems, and environmental controls for optimal operation and troubleshooting.
* **Energy Consumption:** Power is continuously required for pumps, lighting, the rotation motor, and environmental control systems, which can be a significant operational expense.
* **Systemic Failure Risk:** Reliance on mechanical and electrical components means a single point of failure (e.g., pump malfunction, motor breakdown) can impact the entire crop.
* **Maintenance Requirements:** Regular monitoring of nutrient solution parameters (pH, EC), cleaning to prevent algae buildup, and periodic maintenance of mechanical components are necessary.
**Applications:**
Vertical Shelf Rack Tray Rotary Hydroponic Plant Garden Towers are deployed across various sectors:
* **Commercial Vertical Farms:** Large-scale food production facilities in metropolitan areas.
* **Agricultural Research and Development:** Controlled environments for studying plant physiology, genetics, and nutrient uptake.
如果你需要一个不同的格式,请打开一个新的支持票和为此请求。我们可以转换到 3D 模型: .stl, .c4d, .obj, .fbx, .ma/.mb, .3ds, .3dm, .dxf/.dwg, .max. .blend, .skp, .glb. 我们不转换 3d 场景 以及 .step, .iges, .stp, .sldprt 等格式。!
VERTICAL SHELF RACK TRAY ROTARY HYDROPONIC PLANT GARDEN TOWER 3D 模型 iges, 3ds, blend, stl, step, fbx, max, obj, dwg, 3dm, glb, sat, dae, skp, 从 surf3d
aeroponic array tower structure frame multi-layers multi-tier row revolutionary farm wheel spin greenhouse upright produce aquaponic agriculture farming hydroponic vegetableVERTICAL SHELF RACK TRAY ROTARY HYDROPONIC PLANT GARDEN TOWER - You can use this royalty-free 3D model for both personal and commercial purposes in accordance with the Basic or Extended License.
The Basic License covers most standard use cases, including digital advertisements, design and visualization projects, business social media accounts, native apps, web apps, video games, and physical or digital end products (both free and sold).
The Extended License includes all rights granted under the Basic License, with no usage limitations, and allows the 3D model to be used in unlimited commercial projects under Royalty-Free terms.


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 Polska
Polska Français
Français 中國
中國 한국의
한국의 Українська
Українська Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Русский
Русский हिंदी
हिंदी