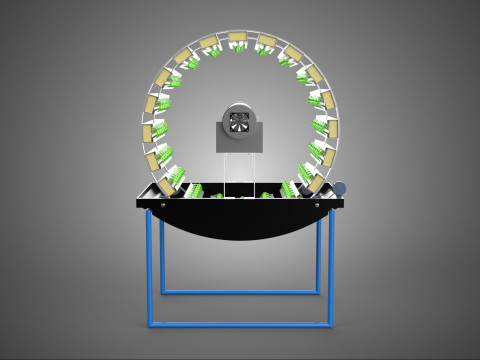
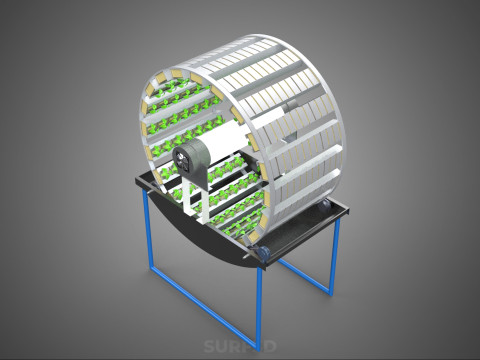
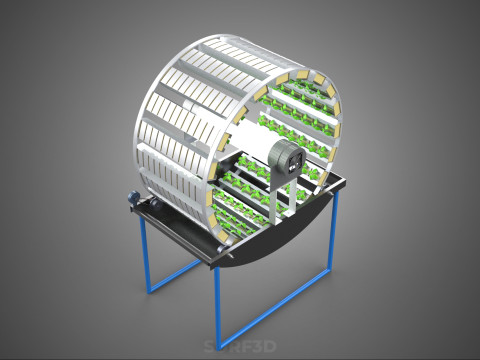
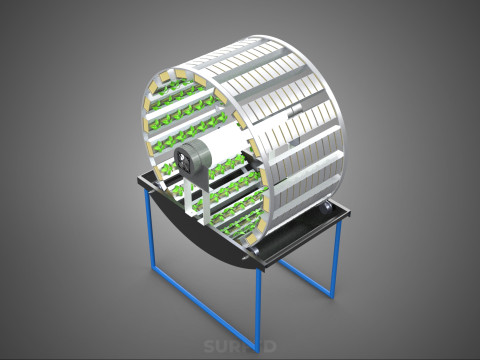
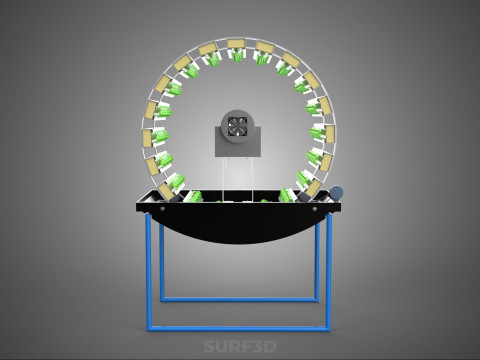
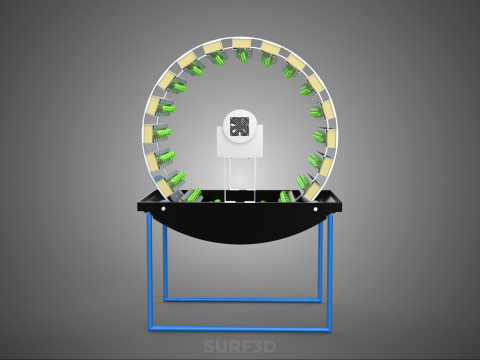
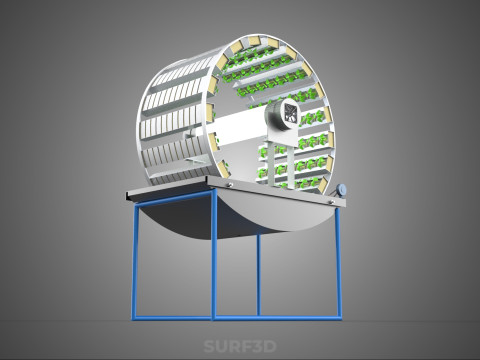
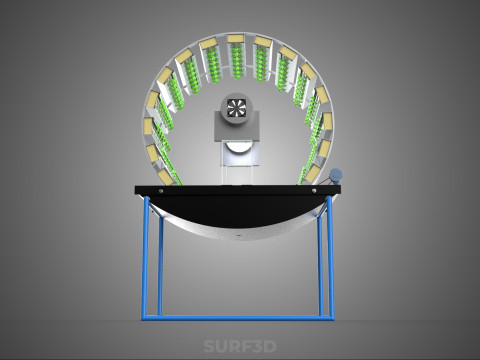
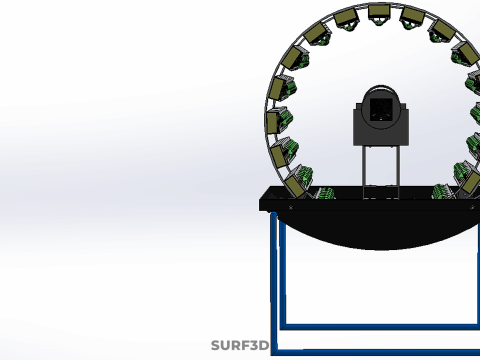
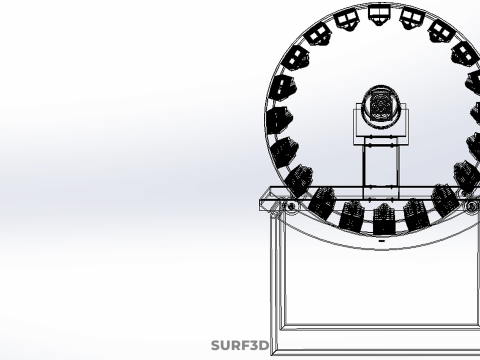
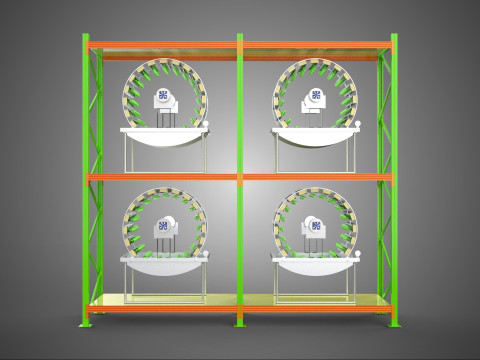
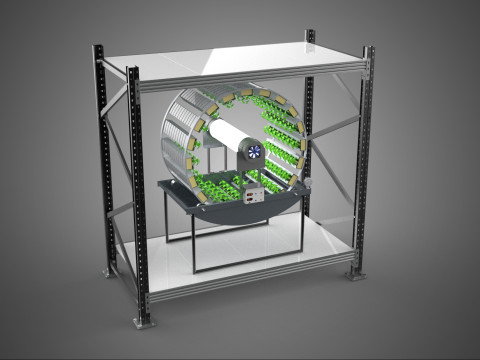
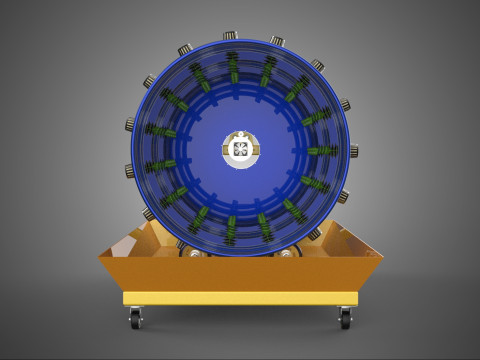
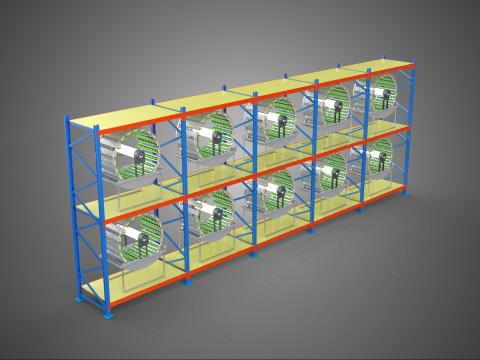
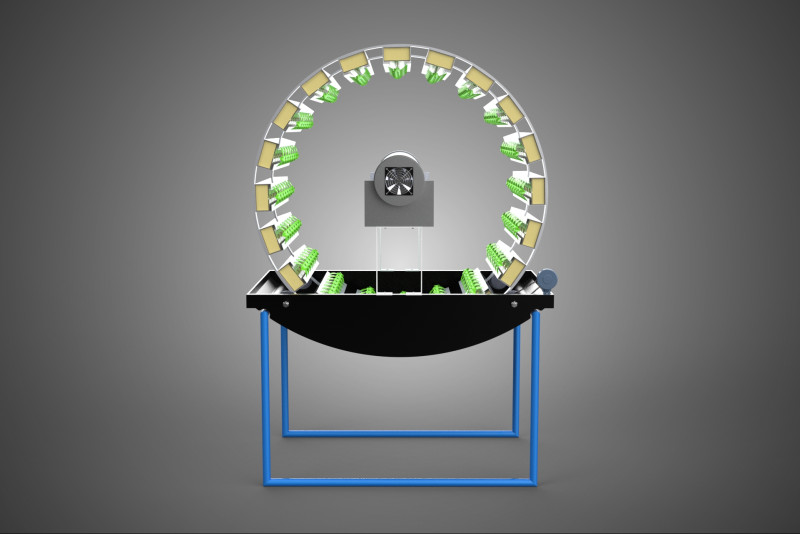
CIRCULAR ROTARY HYDROPONIC SPIN GARDEN PLANT FARM SYSTEM WHEEL Modèle 3D
- Formats disponibles: Rhinoceros (.3dm) 5.01 MBSTEP (.step) 1.48 MBBlender3D (.blend) 18.54 MB3D Studio (.3ds) 7.28 MBSketchUp (.skp) 2.76 MBAutodesk AutoCAD (.dwg) 4.72 MBWavefront OBJ (.obj) 25.80 MBCollada (.dae) 31.00 MBIGES (.iges) 1.67 MBStereolithography (.stl) 26.24 MBAutodesk FBX (.fbx) 37.48 MBACIS(.sat) 8.88 MBAutodesk 3DS MAX (.max) 34.52 MBGLB (.glb / .gltf) 8.31 MB
- Polygones:1639539
- Sommets:1088003
- Animé:No
- Textures:No
- Installé:No
- Matériaux:
- Bas-poly:No
- Collection:No
- cartographie UVW:No
- Plugins Utilisé:No
- Prêt à imprimer:No
- 3D Balayage:No
- Contenu adulte:No
- PBR:No
- IA Formation:No
- Géométrie:Poly NURBS
- UVs non enveloppés:Unknown
- Vus:106
- Date: 2025-09-28
- ID de produit:602013
High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely supported formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software support
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
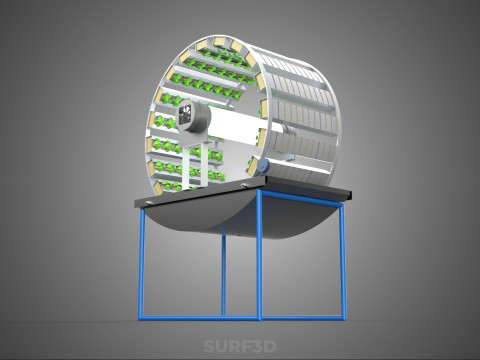
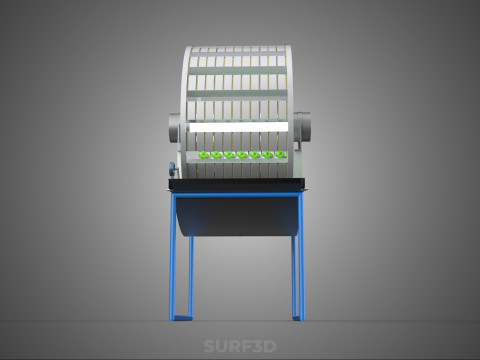
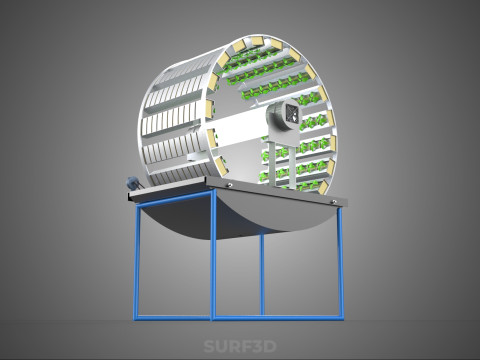
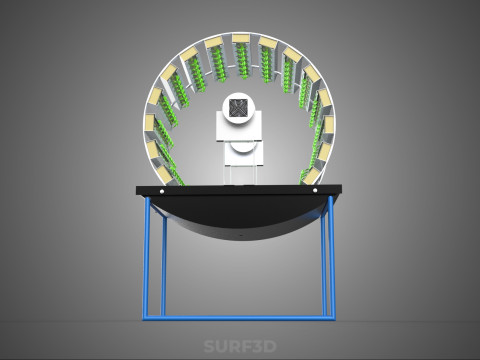
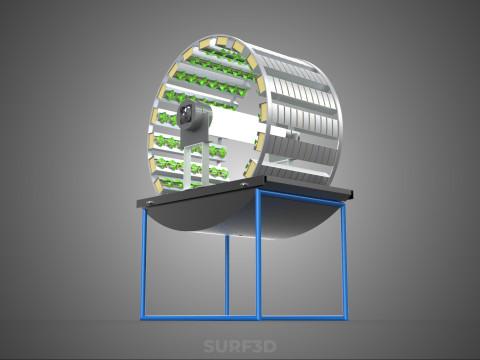
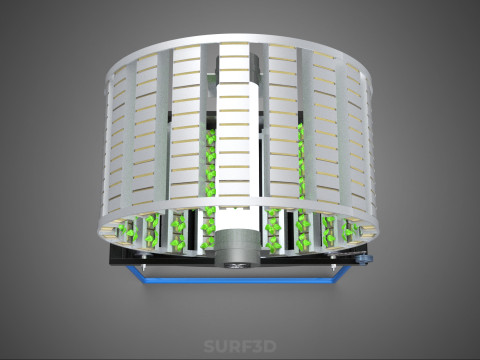
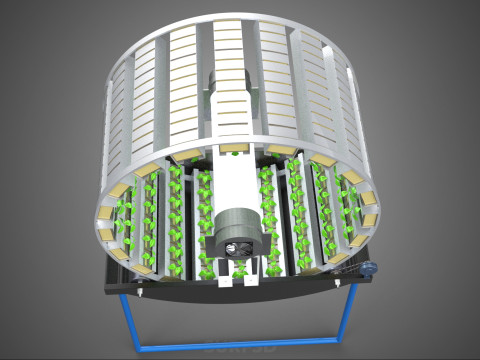
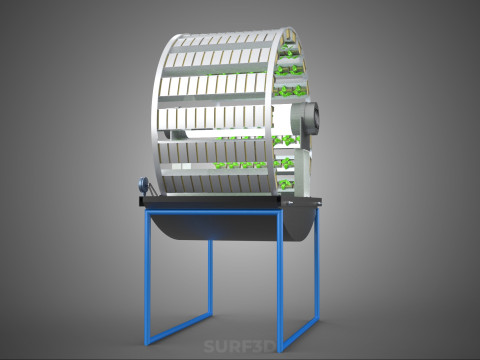
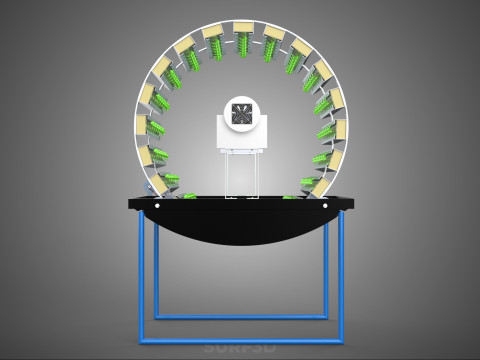
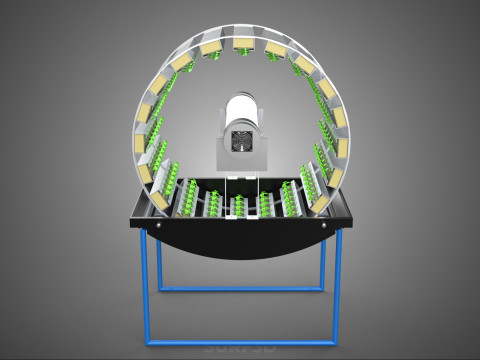
A **Circular Rotary Hydroponic Spin Garden Plant Farm System Wheel** is an advanced controlled environment agriculture (CEA) technology that integrates soilless plant cultivation with a rotating, wheel-shaped physical structure. This innovative system is designed to maximize plant density, optimize resource utilization, and facilitate uniform growth conditions, making it particularly suitable for urban farming, research, and high-efficiency agricultural production in constrained spaces.
**Nomenclature and Core Principles:**
The composite title precisely describes the system's fundamental characteristics:
* **Circular Rotary:** Refers to the system's primary mechanical design, involving a wheel or drum that rotates around a central axis. This rotation is paramount for ensuring equitable distribution of light, air, and nutrients to all cultivated plants.
* **Hydroponic:** Denotes the method of soilless cultivation, where plants obtain essential mineral nutrients from solutions dissolved in water rather than from soil. This approach enables precise nutrient management and significant water savings through recirculation.
* **Spin Garden Plant Farm System:** Highlights its function as a comprehensive plant cultivation apparatus, utilizing the rotational dynamic to grow a variety of crops in a managed, often vertical, configuration.
* **Wheel:** Emphasizes the predominant structural form, which resembles a large wheel or drum with integrated modules for holding plants along its perimeter or within its internal chambers.
**Mechanism and Design:**
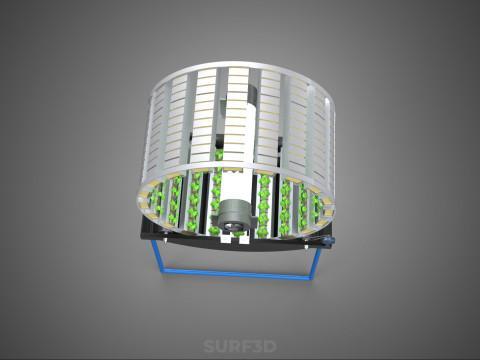
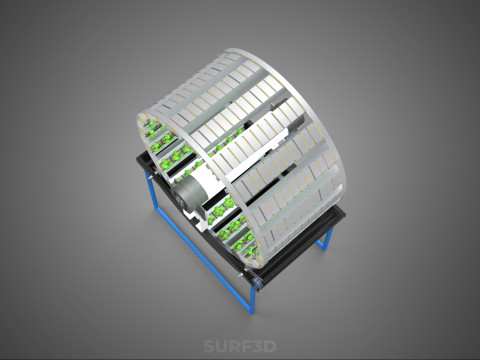
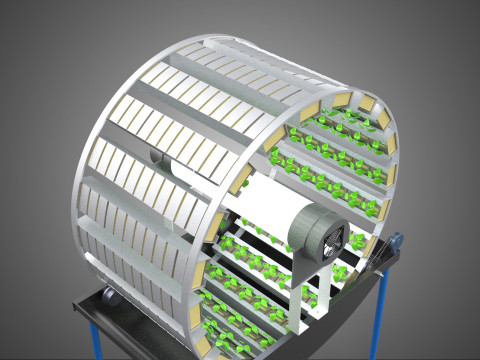
At its operational core, a circular rotary hydroponic system comprises a large wheel or drum, typically mounted on a central axle, which undergoes slow, controlled rotation. Plants are secured in individual grow pots or modules (frequently net pots) embedded into the outer circumference or internal compartments of this wheel. A nutrient reservoir, containing a meticulously formulated hydroponic solution, is generally positioned beneath the rotating structure. As the wheel revolves, the plant roots, extending from their respective modules, are periodically immersed into or misted by this nutrient-rich solution.
Key design elements typically include:
1. **Rotational Mechanism:** An electric motor drives the slow, continuous, or intermittent rotation of the wheel. The rotational speed is precisely calibrated to facilitate optimal nutrient uptake, root aeration, and equitable light exposure for all plants.
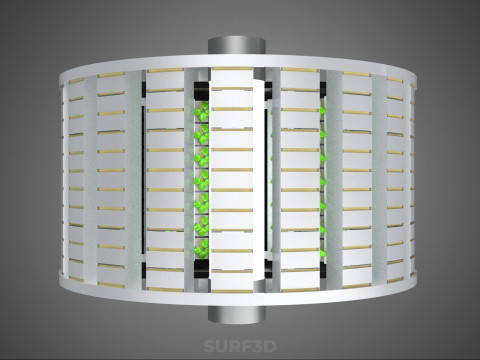
2. **Plant Holding Modules:** These are pockets, baskets, or trays specifically designed to securely cradle plants while allowing their roots to freely extend into the nutrient delivery zone.
3. **Nutrient Delivery System:** Pumps draw the nutrient solution from the reservoir, delivering it to the plant roots. This can be accomplished through various hydroponic techniques, such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC) elements (where roots periodically dip into the solution), or aeroponics (where roots are continuously or intermittently misted with nutrient solution). The system is typically recirculating, minimizing water and nutrient wastage.
4. **Lighting System:** In many "spin garden" designs, a high-efficiency light source (commonly LED grow lights) is strategically positioned centrally within the rotating wheel. This configuration ensures uniform illumination for all plants as they traverse the illuminated zone during rotation. Alternatively, external lighting may be employed in certain larger-scale or specialized configurations.
5. **Environmental Controls:** Advanced systems often incorporate sensors and automated controls for critical environmental parameters, including temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, and the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution. These controls maintain an optimal microclimate conducive to rapid and healthy plant growth.
**Advantages and Applications:**
The circular rotary hydroponic system offers several compelling benefits:
* **Space Efficiency:** Its vertical and rotational design permits significantly higher plant density per unit of floor area compared to traditional horizontal farming, rendering it highly advantageous for urban environments and areas with limited space.
* **Optimized Resource Utilization:**
* **Water:** Hydroponic systems, by recirculating water, can reduce consumption by up to 90% compared to conventional soil-based agriculture.
* **Light:** Centralized or uniformly distributed lighting ensures all plants receive consistent and adequate light intensity, often leading to reduced energy consumption for lighting.
* **Nutrients:** Precise nutrient delivery minimizes waste and ensures plants receive the exact mineral balance required for optimal development.
* **Accelerated Growth Rates and Yields:** Controlled environmental conditions, consistent nutrient availability, and optimized light exposure frequently result in faster growth cycles and enhanced crop yields.
* **Reduced Pest and Disease Incidence:** The soilless, often semi-enclosed nature of these systems inherently reduces exposure to soil-borne pathogens and common pests, potentially minimizing the reliance on pesticides and herbicides.
* **Year-Round Production:** Indoor cultivation dissociates production from seasonal variations and adverse weather conditions, enabling continuous harvesting and a stable supply of fresh produce.
These systems find application in diverse contexts, including large-scale commercial vertical farms, research facilities investigating plant physiology and growth kinetics, educational settings demonstrating sustainable agricultural practices, and increasingly, as compact and efficient solutions for home gardening.
**Variations and Challenges:**
While the "wheel" form is prevalent, variations exist, such as rotating drums or multi-layered cylindrical towers, all adhering to the principle of rotating plants around a central axis or light source. The primary distinctions often lie in the lighting configuration (internal vs. external) and the specific hydroponic technique integrated.
Si vous avea besoin d’\autre format veuillez ouvrir un billet d’\assistance et demandez le. Nous pouvons convertir les modèles de 3D en: .stl, .c4d, .obj, .fbx, .ma/.mb, .3ds, .3dm, .dxf/.dwg, .max. .blend, .skp, .glb. Nous ne convertissons pas les scènes 3D et des formats tels que .step, .iges, .stp, .sldprt.!


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 Polska
Polska Français
Français 中國
中國 한국의
한국의 Українська
Українська Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Русский
Русский हिंदी
हिंदी