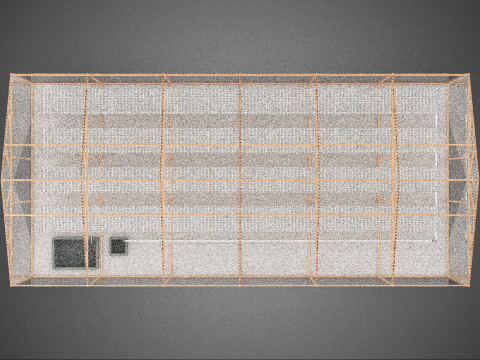
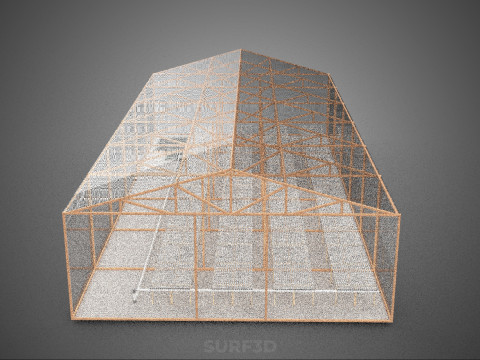
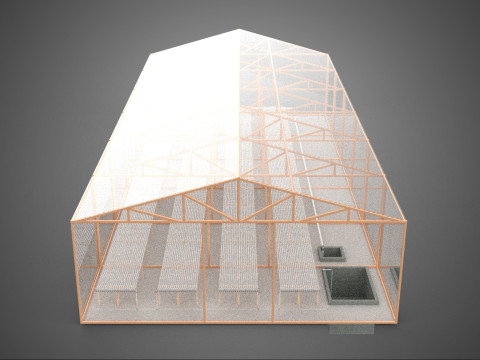
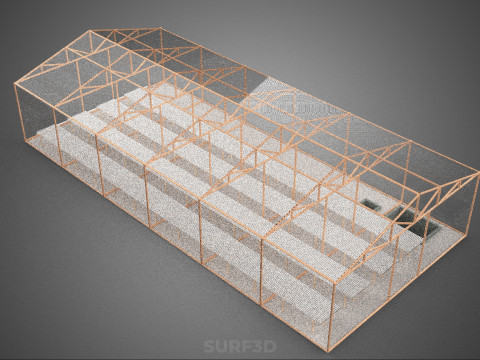
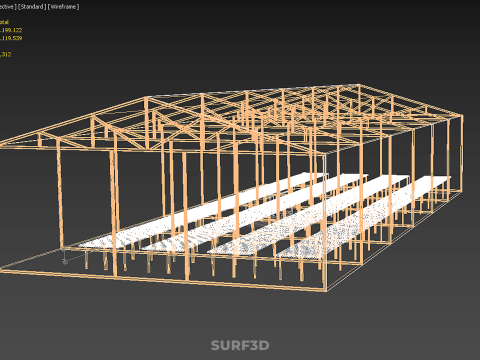
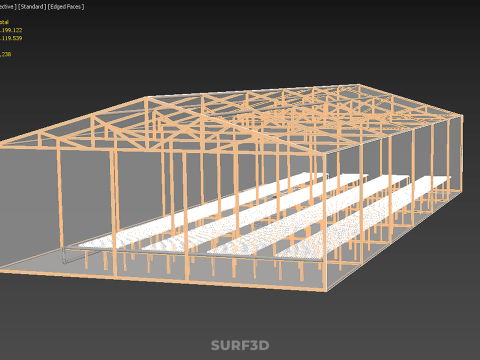
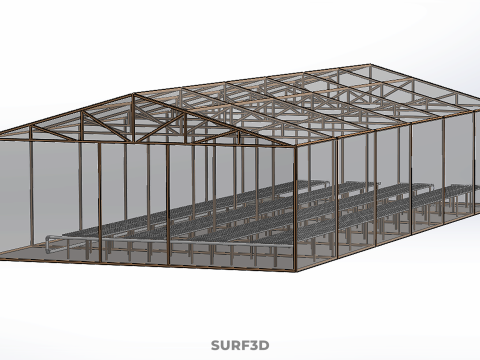
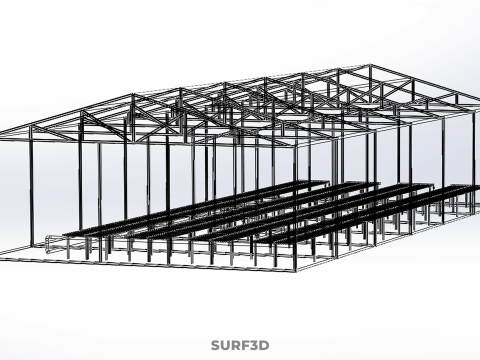
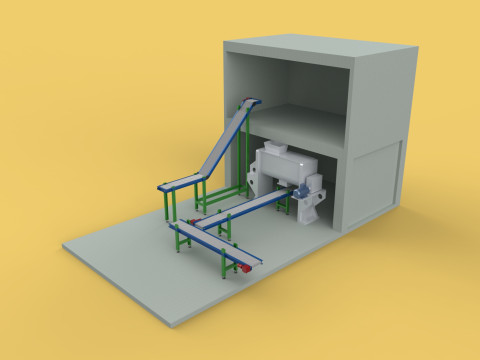
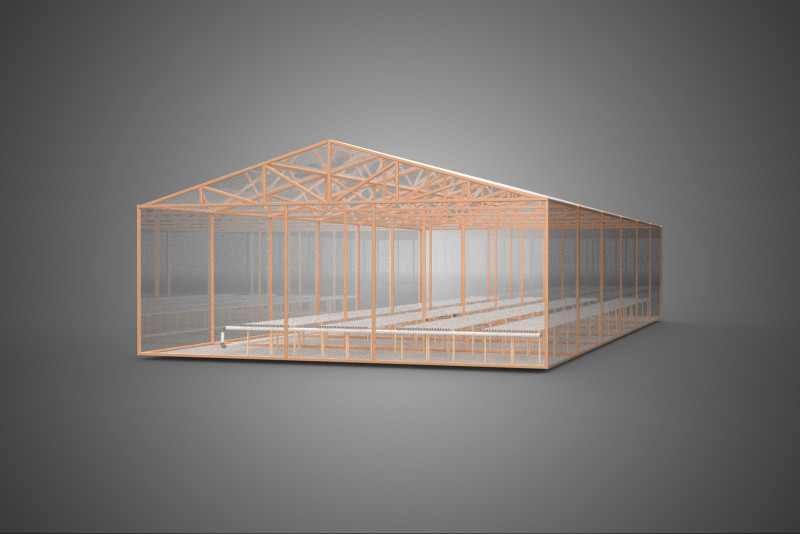
ROLNICTWO UKŁAD BUDYNKU ROLNICTWO SZKLARNIA OGRÓD HYDROPONICZNY Model 3D

- Poproś autora o wsparcie produktu
- Dostępne formaty:
- ID produktu:605273
- Data: 2025-10-14
- Wielokąty:3199122
- Wierzchołki:3119539
- Model animowany:No
- Tekstury:No
- Oparty na szkielecie:No
- Materiał:
- Low-poly:No
- Kolekcja:No
- UVW mapping:No
- Plugins Used:No
- Gotowy do wydruku:No
- 3D Scan:No
- Adult content:No
- PBR:No
- AI Szkolenie:No
- Geometria:Poly NURBS
- Unwrapped UVs:Unknown
- Liczba wyświetleń:214
Opis
High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely supported formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software support
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
An agriculture building designed with a meticulously planned layout for modern farming, specifically integrating greenhouses and hydroponic gardens, constitutes a sophisticated paradigm within Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA). These purpose-built facilities are engineered to provide optimal, regulated conditions for plant cultivation, thereby transcending the limitations imposed by external climatic variability, land availability, and seasonal cycles. Such integrated structures are central to advanced food production, horticultural research, and the burgeoning urban farming movement, addressing critical challenges related to food security, resource conservation, and year-round supply.
The **Agriculture Building** itself serves as the foundational envelope, providing structural integrity, insulation, and the necessary infrastructure to support intensive farming operations. Its internal **Layout** is paramount, dictating operational efficiency, resource flow, and the functional segregation of diverse agricultural processes. A well-conceived layout typically delineates several specialized zones:
1. **Growing Zones:** Primary areas housing the **Greenhouse** and **Hydroponic Garden** systems, optimized for specific environmental parameters (light, temperature, humidity, CO2).
2. **Propagation Areas:** Dedicated sections for seed germination, cloning, and seedling development, often requiring distinct, highly controlled microclimates.
3. **Processing and Packaging Zones:** Areas for harvesting, post-harvest handling, cleaning, sorting, and packaging produce for distribution, designed to maintain product quality and minimize contamination.
4. **Nutrient and Water Management Hubs:** Centralized locations for reservoirs, pumps, filters, water purification systems (e.g., reverse osmosis), and automated nutrient solution mixing stations.
5. **Storage Facilities:** For raw materials (seeds, growing media, nutrients), equipment, and climate-controlled storage for harvested crops.
6. **Utilities and Control Rooms:** Centralized housing for HVAC systems, irrigation controls, electrical infrastructure, lighting ballasts, environmental sensors, and sophisticated monitoring and automation systems.
7. **Administrative and Research Spaces:** Offices, laboratories, and educational areas for personnel, data analysis, and scientific investigation.
The layout is meticulously planned to facilitate linear or circular workflows, minimizing manual labor, reducing cross-contamination risks, and enhancing overall operational safety and productivity. Key design considerations include accessibility for maintenance, strict biosecurity protocols for pest and disease prevention, and the seamless integration of advanced automation technologies.
**Greenhouses** within this context function as sophisticated environmental modifiers for plant growth. These structures, typically featuring transparent or translucent glazing materials (e.g., glass, polycarbonate, polyethylene film), are designed to maximize light penet*ration while providing a controlled internal atmosphere. Modern greenhouses integrate an array of climate control systems, including:
* **Heating and Cooling Systems:** HVAC units, forced air heaters, radiant heating, evaporative coolers, and automated ventilation systems to maintain optimal temperatures.
* **Supplemental Lighting:** High-intensity discharge (HID) lamps or energy-efficient LED grow lights to extend photoperiods or compensate for inadequate natural light, tailored to specific crop spectral requirements.
* **Humidity Management:** Fogging systems, misters, or dehumidifiers to regulate atmospheric moisture levels.
* **CO2 Enrichment:** Injection systems to elevate carbon dioxide concentrations, thereby boosting photosynthetic rates.
* **Shading Systems:** Automated screens or coatings to mitigate excessive solar radiation and prevent heat stress.
These systems operate in concert, often managed by a central building management system (BMS), to create precise, crop-specific microclimates, thereby maximizing growth rates, yield potential, and produce quality.
The **Hydroponic Garden** component refers to the application of soilless cultivation techniques within these controlled greenhouse environments. Hydroponics offers substantial advantages over conventional soil-based agriculture, including a dramatic reduction in water consumption (often up to 90% less through recirculation), accelerated growth cycles, higher plant densities per unit area, and the complete elimination of soil-borne pests and diseases. Common hydroponic systems deployed in such facilities include:
* **Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):** Plants are grown in shallow channels over which a thin film of recirculating nutrient solution continuously flows.
* **Deep Water Culture (DWC):** Plant roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich, oxygenated solution within a reservoir.
* **Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain):** Growing beds or trays are periodically flooded with nutrient solution and then drained back into a reservoir.
* **Drip Systems:** Nutrient solution is delivered directly to the base of each plant via precise emitters, often used with inert growing media (e.g., rockwool, coco coir).
* **Aeroponics:** Plant roots are suspended in air within an enclosed environment and intermittently misted with a fine spray of nutrient solution.
The selection of a specific hydroponic system is contingent upon factors such as crop type, desired scalability, operational complexity, and resource efficiency targets. These systems necessitate meticulous management of the nutrient solution's composition (pH, electrical conductivity, specific ion concentrations), temperature, and dissolved oxygen levels to ensure optimal plant health, nutrient uptake, and overall productivity.
Potrzebujesz plik w innym formacie?
Jeśli potrzebny Ci plik w innym formacie, zgłoś taką potrzebę przez opcję Support Ticket Konwertujemy produkty na następujące formaty: .stl, .c4d, .obj, .fbx, .ma/.mb, .3ds, .3dm, .dxf/.dwg, .max. .blend, .skp, .glb. Dowolna konwersja formatuNie konwertujemy scen 3D oraz formaty takie jak .step, .iges, .stp, .sldprt.!
Informacje o użytkowaniu
ROLNICTWO UKŁAD BUDYNKU ROLNICTWO SZKLARNIA OGRÓD HYDROPONICZNY - Możesz używać tego bezpłatnego modelu 3D zarówno do celów osobistych, jak i komercyjnych, zgodnie z Licencją Podstawową lub Rozszerzoną.Licencja Podstawowa obejmuje większość standardowych przypadków użycia, w tym reklamy cyfrowe, projekty projektowe i wizualizacyjne, firmowe konta w mediach społecznościowych, aplikacje natywne, aplikacje internetowe, gry wideo oraz fizyczne lub cyfrowe produkty końcowe (zarówno bezpłatne, jak i sprzedawane).
Licencja Rozszerzona obejmuje wszystkie prawa udzielone na mocy Licencji Podstawowej, bez ograniczeń użytkowania i pozwala na wykorzystanie modelu 3D w nieograniczonej liczbie projektów komercyjnych na warunkach bezpłatności.
Czytaj więcej


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 Polska
Polska Français
Français 中國
中國 한국의
한국의 Українська
Українська Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Русский
Русский हिंदी
हिंदी