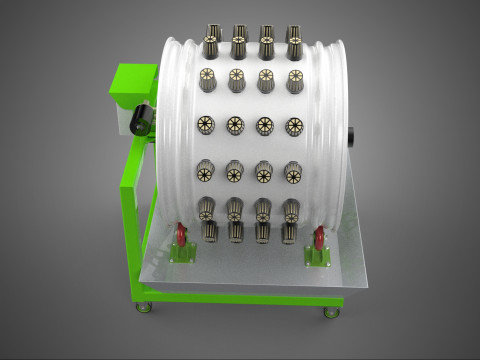
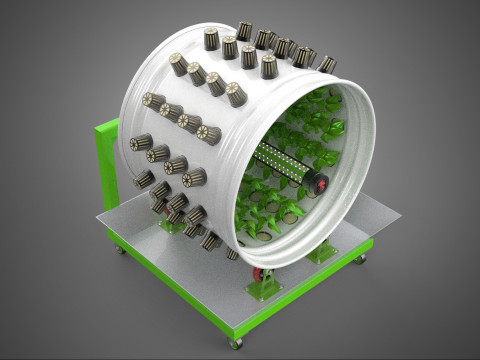
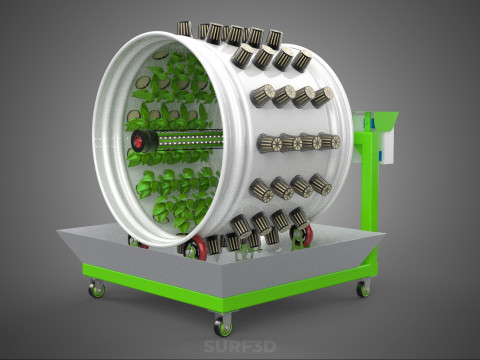
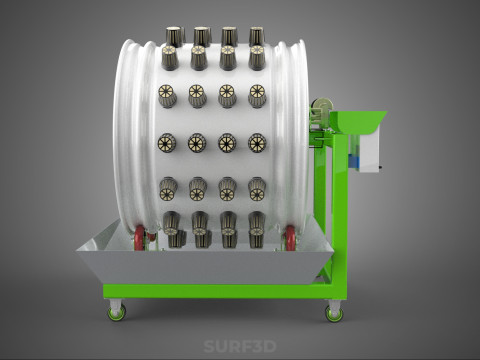
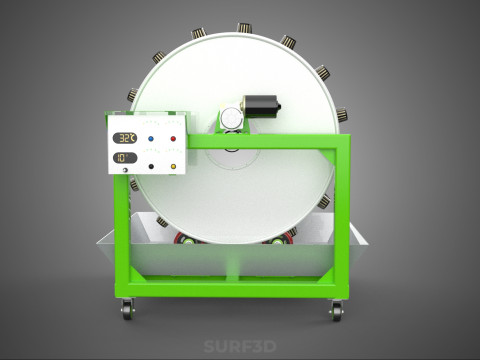
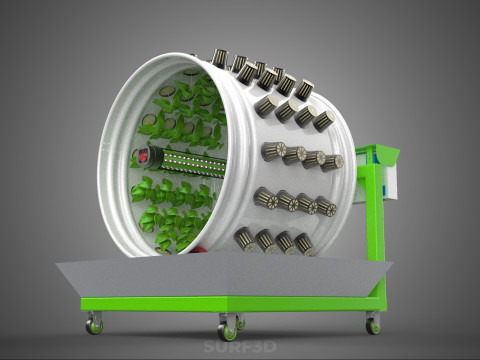
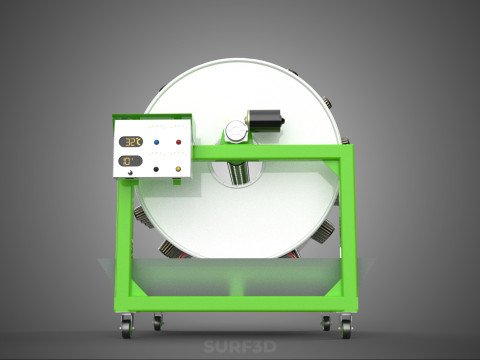
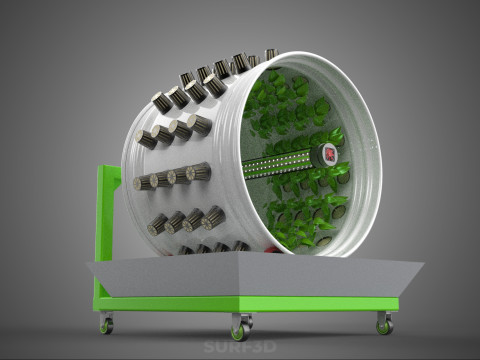
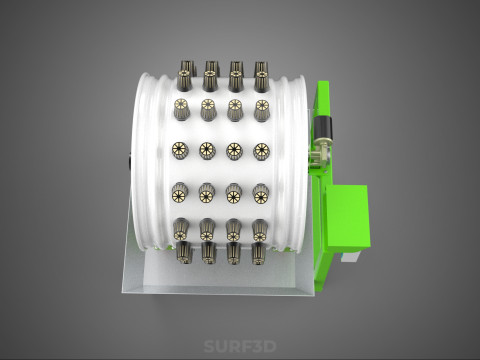
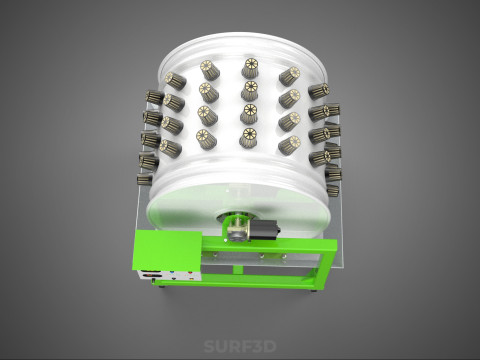
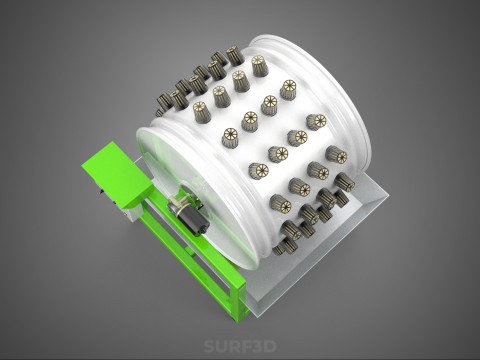
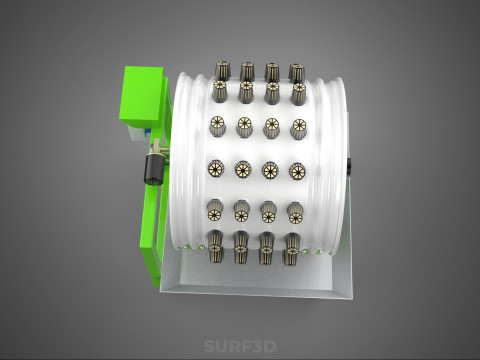
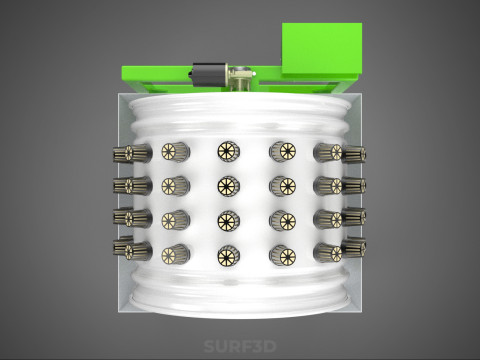
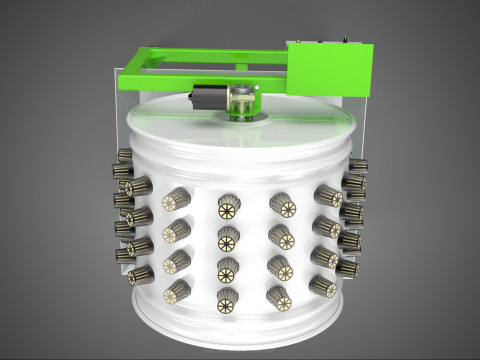
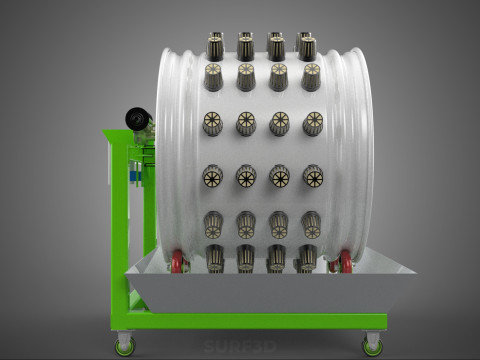
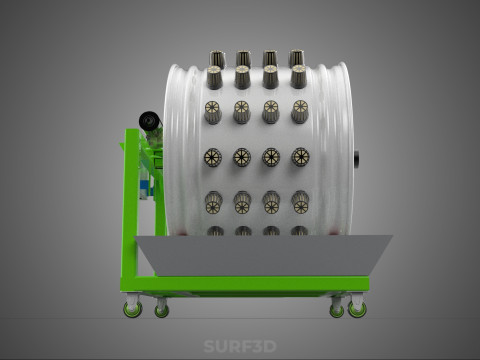
ROTARY HYDROPONIC RADIAL SPIN GARDENING PLANT FARM SYSTEM WHEEL 3D Model

- Request product support by the author
- Available formats:
- Item ID:603003
- Date: 2025-10-03
- Polygons:3041833
- Vertices:2305040
- Animated:No
- Textured:No
- Rigged:No
- Materials:
- Low-poly:No
- Collection:No
- UVW mapping:No
- Plugins Used:No
- Print Ready:No
- 3D Scan:No
- Adult content:No
- PBR:No
- AI Training:No
- Geometry:Poly NURBS
- Unwrapped UVs:Unknown
- Views:246
Description
High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely *******ed formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software *******
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
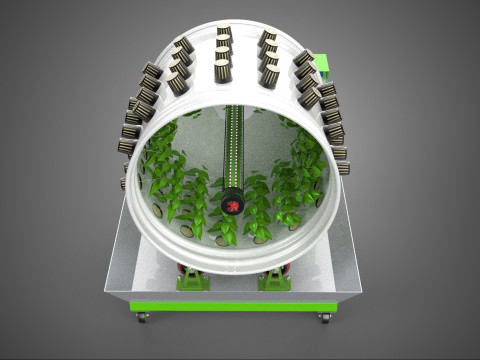
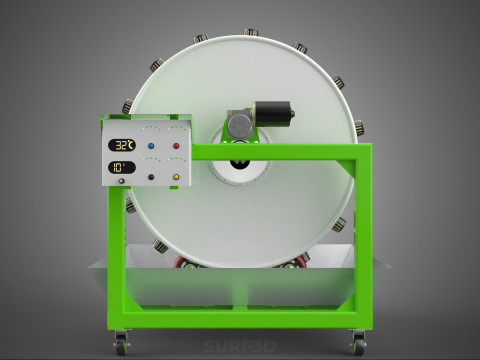
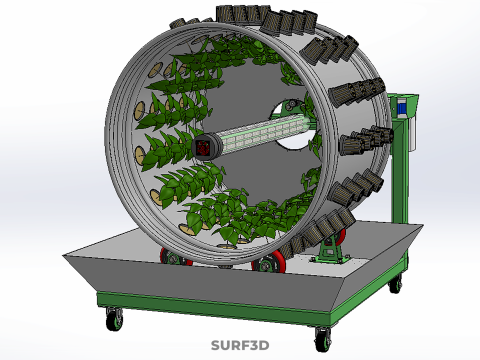
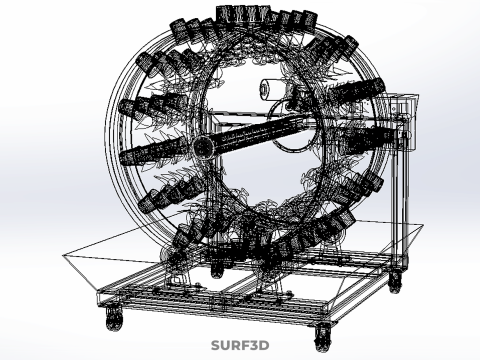
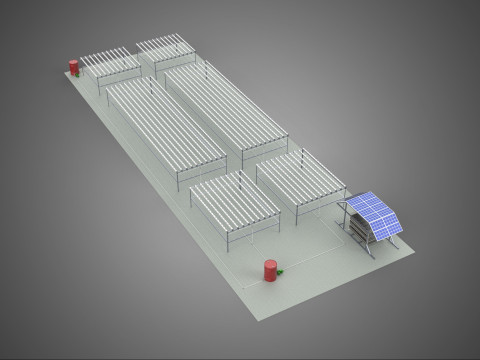
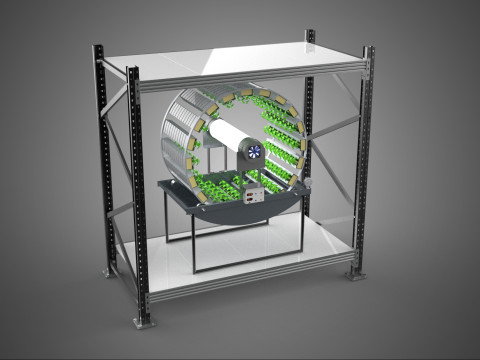
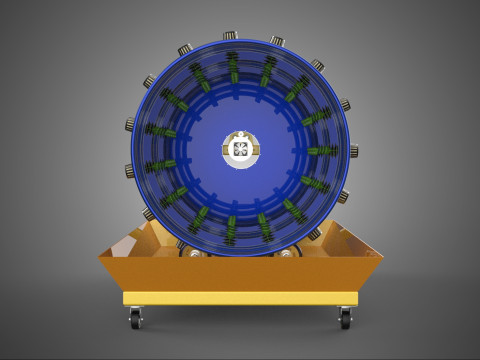
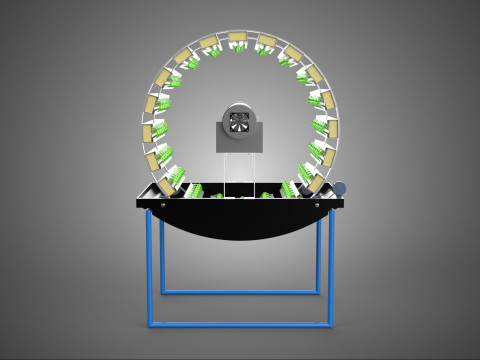
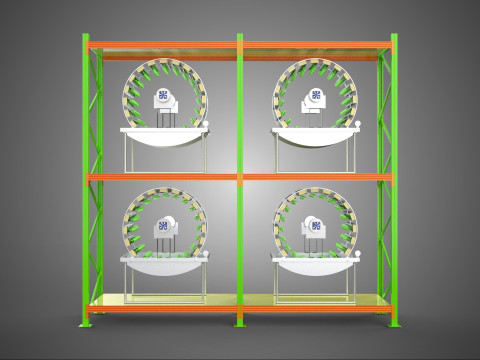
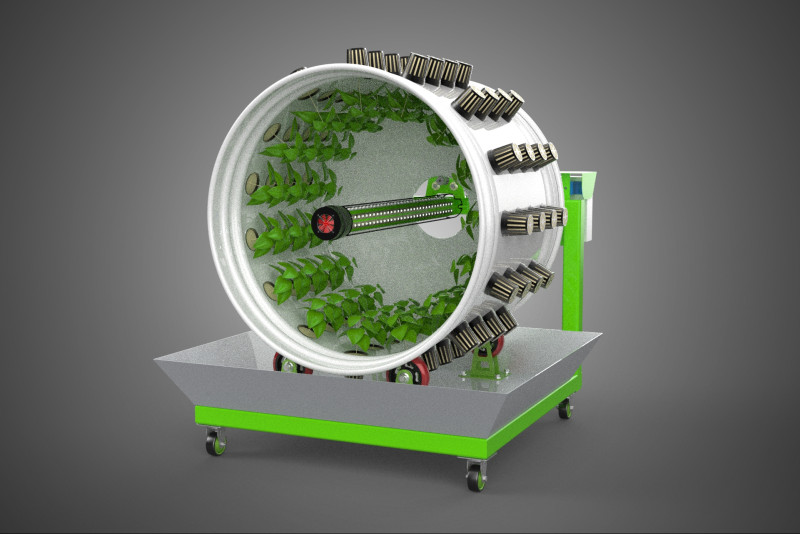
The Rotary Hydroponic Radial Spin Gardening Plant Farm System Wheel, often referred to as a rotary hydroponic system or a hydroponic grow wheel, is an advanced agricultural technology that integrates soilless hydroponic cultivation with a dynamic, rotating structural design. This system is engineered to maximize plant growth within a confined footprint by orienting plants radially around a central axis, typically a primary light source, and continuously or intermittently rotating them.
**Nomenclature Breakdown:**
* **Rotary:** Denotes the system's characteristic rotational movement, usually around a central light source or for optimized nutrient distribution.
* **Hydroponic:** Specifies the method of soilless cultivation, where plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions rather than soil.
* **Radial Spin Gardening:** Describes the arrangement of plants extending outwards from a central point, similar to spokes on a wheel, with the entire structure or individual plant sites undergoing controlled rotation.
* **Plant Farm System:** Identifies it as a comprehensive setup designed for the high-density cultivation of multiple plants for agricultural or horticultural purposes.
* **Wheel:** Refers to the circular or cylindrical structure that houses the plants and facilitates the rotational mechanism.
**Core Principles of Operation:**
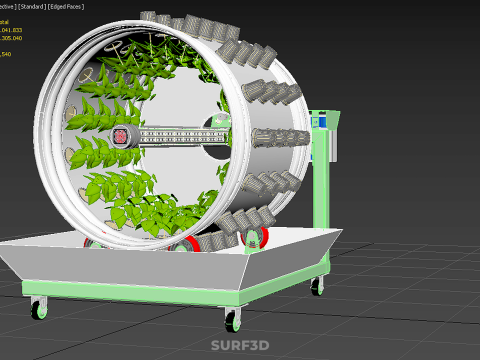
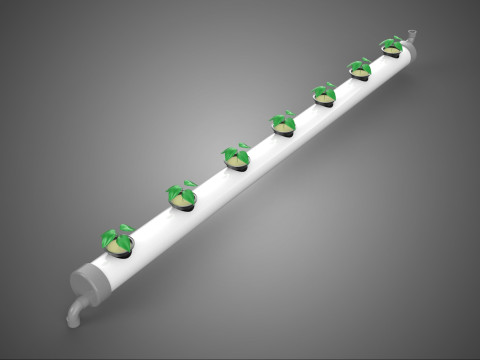
The operational efficacy of a rotary hydroponic radial spin system hinges on the synergistic application of hydroponics and controlled rotation. Plants are typically anchored in inert growing media, such as rockwool, coco coir, or clay pebbles, within net pots or similar containers embedded in openings around the circumference of a large, wheel-shaped structure. A nutrient reservoir situated beneath or adjacent to the wheel supplies a precisely balanced aqueous solution to the plants' roots. Nutrient delivery mechanisms commonly include drip irrigation, nutrient film technique (NFT), or direct root immersion.
The defining characteristic is the programmed rotation of the wheel. In most designs, a powerful, high-intensity light source (e.g., LED or HID lamp) is positioned at the hub of the wheel. As the wheel rotates, each plant is periodically exposed to this central light, ensuring uniform illumination across the entire crop and optimizing photosynthetic efficiency. This rotational movement also facilitates consistent nutrient delivery to all plant roots as they pass through or are sprayed with the nutrient solution. Furthermore, the constant repositioning can aid in air circulation around the foliage, contributing to plant health and potentially reducing the incidence of fungal diseases.
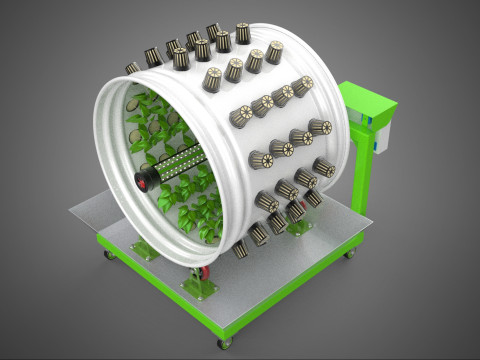
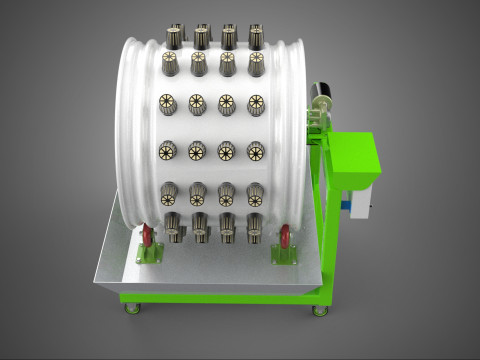
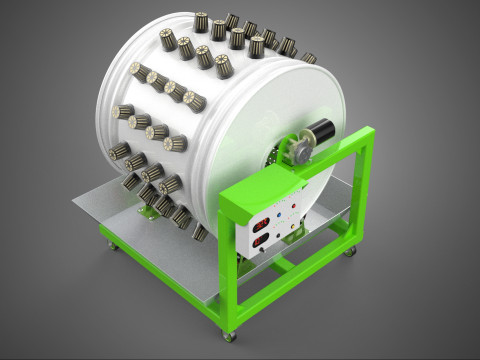
**Key Components:**
A typical Rotary Hydroponic Radial Spin System Wheel comprises several integral components:
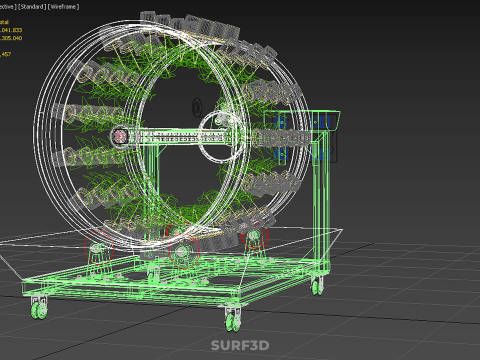
1. **Wheel Structure:** The primary circular or cylindrical frame, often constructed from durable, food-grade materials like PVC, ABS, or coated metal, which provides structural integrity and holds the individual plant sites.
2. **Plant Sites:** Recesses, pockets, or net pot holders integrated into the wheel's circumference where plants are secured.
3. **Nutrient Reservoir:** A tank designed to store the precisely formulated water and dissolved mineral nutrient solution.
4. **Water Pump & Delivery System:** A submersible pump circulates the nutrient solution from the reservoir to the plant roots, typically through tubing, sprayers, or wicking elements.
5. **Central Light Source:** A high-intensity lamp (e.g., full-spectrum LED grow lights, HPS, MH) strategically positioned at the center of the wheel to provide uniform light to all radially arranged plants.
6. **Motor & Drive System:** An electric motor coupled with gears, belts, or direct drive mechanisms responsible for the controlled, continuous, or intermittent rotation of the wheel.
7. **Environmental Controls:** Sensors and automated controllers for monitoring and regulating critical parameters such as pH, Electrical Conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution, ambient temperature, humidity, and the speed/timing of wheel rotation.
**Advantages:**
The adoption of rotary hydroponic radial spin systems offers several significant benefits:
* **Space Efficiency:** Maximizes the number of plants grown per unit of floor space by utilizing vertical and radial dimensions, making it highly suitable for urban farming, indoor cultivation, or areas with limited land.
* **Accelerated Growth Rates:** Controlled environmental conditions, optimized nutrient delivery, and uniform light exposure often lead to faster plant growth cycles and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based methods.
* **Resource Conservation:** Hydroponic systems inherently use significantly less water (up to 90% less) than conventional soil agriculture due to water recirculation. Targeted nutrient delivery also minimizes fertilizer waste.
* **Uniform Light Exposure:** The rotational movement ensures that all sides of each plant receive consistent and optimized light, promoting even growth and preventing etiolation.
* **Reduced Pests and Diseases:** The soilless, enclosed, and controlled environment minimizes exposure to soil-borne pathogens and pests, potentially reducing or eliminating the need for chemical pesticides.
* **Year-Round Cultivation:** Allows for continuous growing cycles independent of external climate conditions, enabling consistent production.
**Disadvantages and Considerations:**
Despite its benefits, the implementation of such a system presents certain challenges:
* **Initial Capital Cost:** The sophisticated engineering, specialized components, and automation required result in a higher upfront investment compared to simpler hydroponic or soil gardening setups.
* **Technical Complexity:** Requires a greater understanding of hydroponics, plant physiology, mechanical systems, and electrical components for successful operation, monitoring, and maintenance.
* **Energy Consumption:** The continuous operation of pumps, motors, and high-intensity grow lights can lead to significant electricity usage, impacting operational costs.
Need more formats?
If you need a different format, please send us a Conversion Request. We can convert 3D models to: .stl, .c4d, .obj, .fbx, .ma/.mb, .3ds, .3dm, .dxf/.dwg, .max. .blend, .skp, .glb. Free Format ConversionWe do not convert 3d scenes and solid formats such as .step, .iges, .stp, .sldprt etc!
Usage Information
ROTARY HYDROPONIC RADIAL SPIN GARDENING PLANT FARM SYSTEM WHEEL - You can use this royalty-free 3D model for both personal and commercial purposes in accordance with the Basic or Extended License.The Basic License covers most standard use cases, including digital advertisements, design and visualization projects, business social media accounts, native apps, web apps, video games, and physical or digital end products (both free and sold).
The Extended License includes all rights granted under the Basic License, with no usage limitations, and allows the 3D model to be used in unlimited commercial projects under Royalty-Free terms.
Read more


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 Polska
Polska Français
Français 中國
中國 한국의
한국의 Українська
Українська Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Русский
Русский हिंदी
हिंदी